Pink-backed Pelican
Pelecanus rufescens - Pélican gris
Identification
The smallest of the Pelicans of the Western Palearctic. General dirty appearance. Pale gray tinted with pink on the back and, less prominently, underneath the wings. Outside the breeding season, the pouch skin is grayish and becomes reddish-orange during the nuptial period. The eye is bordered in black. The legs are variable in color. The young are brown above. Can be mistaken for the White Pelican (Pelecanus onocrotalus) which is much larger and has a much lighter general appearance. The risks are greater with the Dalmatian Pelican (Pelecanus crispus), larger and with more contrasting wings (black and white rather than black and gray).
Subspecific information monotypic species
Foreign names
- Pélican gris,
- Pelícano rosado,
- pelicano-cinzento,
- Rötelpelikan,
- vörhenyes gödény,
- Kleine Pelikaan,
- Pellicano rossiccio,
- rosaryggig pelikan,
- Rosenpelikan,
- pelikán červenkavý,
- pelikán africký,
- Rosapelikan,
- afrikanpelikaani,
- Kleinpelikaan,
- pelicà rosat,
- Rauðkani,
- pelikan mały,
- Āfrikas pelikāns,
- črnooki pelikan,
- Розовоспинный пеликан,
- コシベニペリカン,
- 粉红背鹈鹕,
- 粉紅背鵜鶘,
Voice song and cries
Habitat
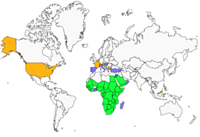
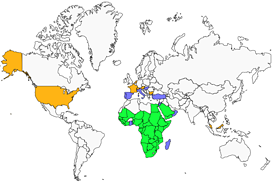
This species is mainly found in freshwater (large lakes, wide rivers), but also in estuaries and saline lakes. The presence of trees is very important. It is a common species in Africa, from south of the Sahara to the Durban region in South Africa, where it is rare. In France, birds from the Sigean Zoo are very often seen fishing in the Narbonne and Gruissan (Aude) region. Until now, no breeding in the wild has been observed in our country.
Behaviour character trait
The Pink-backed Pelican is a gregarious species when breeding but typically fishes individually, occasionally in small groups.
At night it groups together to roost on cliff faces, flat terrain such as islands or calm sites (we saw this in a lagoon in South Africa...). The species seems to remain resident when the environmental conditions remain favourable. Immature individuals may disperse quite far from breeding sites. Occasional observations have been made in Egypt and Israel.The main food source for the Pink-backed Pelican is fish. It will plunge its head beneath the surface and fill its gular pouch with fish and water. It then expels the water from the end of its beak and swallows the fish.
Flight
Dietfeeding habits
Reproduction nesting
While other species of pelicans nest on the ground or in reeds, the Pink-backed Pelican nests in trees (most often with their feet in the water), sometimes next to storks or herons. They lay 2-3 white eggs which are incubated for 30 days. The young can fly after around 3 months, and remain dependant on their parents for up to 3 weeks.
Threats - protection
IUCN conservation status
concern
in the Wild
threatened
evaluated
The Pink-backed Pelican does not seem to be threatened even though a decrease in its population has been observed in some countries. Tourism disturbance and the destruction of favorable environments (fire, deforestation by elephants, among others) are the main causes.
Sources of information
- IOC World Bird List (v14.1), Gill, F and D Donsker (Eds). 2024-04-18.
Other sources of interest
 Specification sheet created on
30/07/2023 by Georges Olioso
Specification sheet created on
30/07/2023 by Georges OliosoTranslation by AI Oiseaux.net
published: 23-07-2005 - Updated: 22-03-2009
© 1996-2024 Oiseaux.net
- Accipitriformes
- Aegotheliformes
- Anseriformes
- Apodiformes
- Apterygiformes
- Bucerotiformes
- Caprimulgiformes
- Cariamiformes
- Casuariiformes
- Charadriiformes
- Ciconiiformes
- Coliiformes
- Columbiformes
- Coraciiformes
- Cuculiformes
- Eurypygiformes
- Falconiformes
- Galliformes
- Gaviiformes
- Gruiformes
- Leptosomiformes
- Mesitornithiformes
- Musophagiformes
- Nyctibiiformes
- Opisthocomiformes
- Otidiformes
- Passeriformes
- Pelecaniformes
- Phaethontiformes
- Phoenicopteriformes
- Piciformes
- Podargiformes
- Podicipediformes
- Procellariiformes
- Psittaciformes
- Pterocliformes
- Rheiformes
- Sphenisciformes
- Steatornithiformes
- Strigiformes
- Struthioniformes
- Suliformes
- Tinamiformes
- Trogoniformes